
Packaging designed to maintain sterility of medical devices needs to comply with several requirements. Package validation testing ensures that the packaging provides physical protection and maintains its sterility. One of the specifications includes a validation test on sealed packaging.
Several techniques can be applied. The primary method is a peel test on the 2 bonded materials. This can be summarized by measuring the force required to separate the two sealed materials, which is equivalent to the opening force of the packaging.

In the medical packaging industry, the validation tests are specified by the ISO 11607 standard ("Packaging for terminally sterilized medical devices"). This standard is the primary guide for medical packaging validation. It is required for both FDA and CE marking certification. Packaging which meets this standard ensures that the object it contains is sterilized and protected. The main requirements of this standard are stability, strength, integrity and dynamic performance testing.
One part of the standard focuses on the strength of the packaging’s seals. It calls for a peel test on the sealed packaging:
- In Europe: EN 868-5 (annex-D) - Packaging for terminally sterilized medical devices. Sealable pouches and reels of porous and plastic film construction. Requirements and test methods.
- In the USA: ATM F88 - Standard test method for seal strength of flexible barrier materials
The U.S. and European standards are similar, but their test methods, the presentation of the results and their acceptance criteria differ.
EN868-5 – Annexe D
This test involves cutting a 15mm wide strip on the package and using a motorized tensile testing machine to separate the two sealed materials. The strip must be cut perpendicular to the seal. A sample of each packaging seal must be collected and tested at its center (see diagram below):
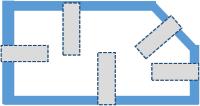
The tensile tester is programmed to run at a speed of 200mm/min and records the force. The force should be at least equal to 1.5N for a 15mm seal. If one of the packaging seals is below this limit, the the package did not conform.
The result report must include the following data:
- The date
- A reference of the tested product
- The maximum recorded strength in N for 15mm width
- Reference of the tensile tester used
- The acquisition rate of the tensile tester
- The curve of the load
- A description of the technique used: supported or unsupported sample
- Identification of the standard used for the test
ASTM F88
This standard offers the benefit of being applicable to a larger number of products than the previously described en868-5 Annex D test (i.e. bonded, flexible or rigid materials) and addresses additional relevant technical points (medium strength, different testing techniques, etc.). However it does not specify a minimum force to be respected.
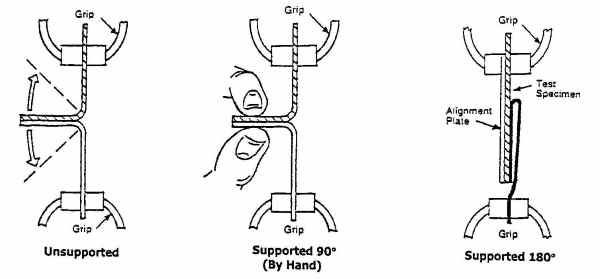
These are a variety of different peel tests:
The spec also allows for the use of various width samples:
- 25 mm (0.984 in)
- 15 mm (.561 in) -> identical to the EN868-5 standard
- 25.4 mm (1 in)
And several speeds: 200 to 300 mm/min (8 to 12 in/min)
The technique to hold (or grip) the sample is precisely described:
- A length of 76 mm (3 in), is recommended for each strip (can be shortened depending upon the type of jaw used)
- A 10mm start distance between the fixtures is recommended for very flexible materials; 25mm for others
- The sealed should be equidistant between the grips and the center the test strip (laterally in the grips)
The result report shall at least include the following data:
- Maximum force in N/m or lb/in
- Mode of failure
- Average force (optional)
- Curve of the test
- Speed rate of separation
- Strip width
- Number of sample tested
- The test technique used: supported or unsupported sample
- Reference of the tested product
- Reference of the tensile tester used
Comparison summary of both standards :
| EN 868-5 | ASTM F88 | |
| Samples | 15 | 25mm, 15mm or 1in |
| Speed of separation | 200 mm/min | 200 to 300 mm/min |
| Technique used | Supported or unsupported sample | Unsupported sample, unsupported at 90° or 180° |
| Results | Maximum force with one minimum | Maximum load, average (optional) and failure mode |
Each standard is different due to sample size and the speed rate of separation but studies show that both methods produce similar results. Especially, regarding the maximum load when the data is converted to equivalent width test strips. Results cannot be differentiated by the speed or the sample width.
Here (below) are a few photos of seal quality peel test machines:
 |  |
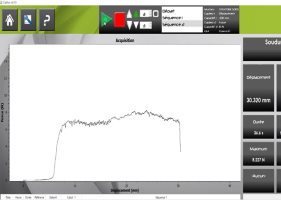 |
This video shows: Seales pouches, porous reels, plastic film
